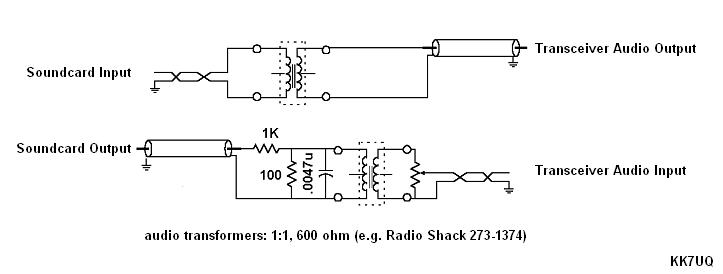
Transceiver-to-Soundcard Audio and Soundcard-to-Transceiver Audio connections
Connecting Soundcards to Transceivers
- recommended circuit
- if your transceiver provides audio input and output signals on a backpanel connector, use these in preference to the front panel microphone and headphone jacks
- this eliminates the need to change connections when switching between digital modes and voice modes
some transceivers must be set to PKT or Data mode if the soundcard audio output is connected to an input other than the microphone input
- If you use your transceiver's a microphone input,
- an audio transformer for isolation is essential
- do not connect the microphone ground to the PTT ground
Soundcard Configuration
WinWarbler enables you to select separate soundcard devices for transmission and reception. On the Config window's Soundcard tab, the PSK & RTTY Reception panel displays up 16 installed input devices, and the Transmission panel displays up to 16 installed output devices. In the Transmission panel, separate PSK & RTTY and Phone sub-panels provide the option of selecting separate soundcard output devices.
If you're using Windows 10, enable Let apps use my microphone in the Settings window's Microphone section. If this option is disabled, applications will be prevented from using any audio device.
If you're using Windows 11, in the Settings window's Privacy & Security section, open the Microphone sub-section and enable
Microphone access
Let apps access your microphone
Let desktop apps access your microphone
Unless the above three options are enabled, applications will be prevented from using any audio device.
The software installed with some soundcards includes a graphic equalizer that can reduce your soundcard's audio output level; if such a capabilities is provided, either disable it, or configure it for no reduction on all frequencies.
Note that Windows will alert you to various events by playing sounds on the soundcard you designate as the default Windows soundcard. To prevent such sounds from being transmitted while you are operating in PSK, RTTY, or Phone, install a second soundcard for use with these modes, and configure the first soundcard to serve as the default Windows soundcard.
Further note that the E-MU 0202 audio interface should be avoided.
Tranceiver-specific considerations
When connected to your PC via its Universal Serial Bus (USB) connection,
the Icom IC-7100, Icom IC-7200, Icom IC-7300, Icom IC-7410, Icom IC-7600, and Icom IC-9100 provide access to both their audio input and audio output by emulating a soundcard. Setup instructions are provided here.
the Kenwood TS-590, Kenwood TS-590SG, and Kenwood TS-900 provide access to both their audio input and audio output by emulating a soundcard. Setup instructions are provided here.
The Kenwood TS-480 can accept audio input from either its front panel MIC input or from the ANI (pin 1) input of its backpanel DATA connector.
to accept audio input from the MIC input, uncheck the DTS transmission using ANI input box in the Radio panel on the General tab of Commander's Configuration window
to accept audio input from the ANI input, check the DTS transmission using ANI input box in the Radio panel on the General tab of Commander's Configuration window.
The Kenwood TS-2000 provides an audio input signal named PKD on pin 11 of its backpanel ACC2 connector. However, PKS is only used as a source if the connector's PKD signal on pin 9 is used for RX-TX switching. Thus if you're connecting your soundcard's audio output to PKS, you cannot use transceiver control software (e.g. Commander) to effect RX-TX switching; you must use a serial port modem control signal to drive PKD via an external circuit.
Additional Information
Setting up CW, Phone, PSK, and RTTY Operation